
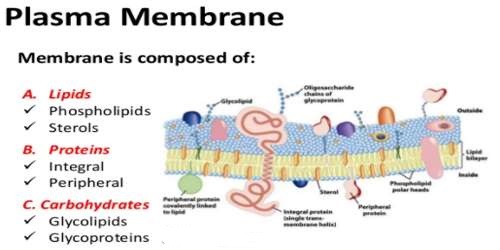
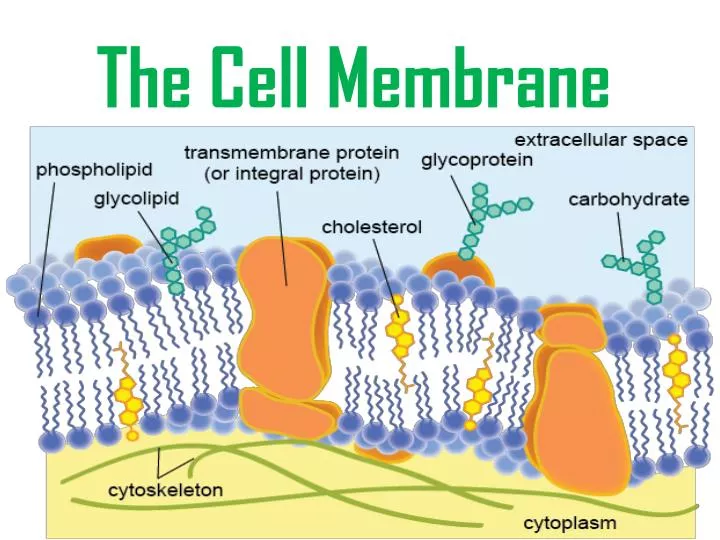
Enclosed by this cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) are the cell’s constituents, often large, water-soluble, highly charged molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and substances involved in cellular metabolism. Glycolysis, electron transport chain, Krebs cycle. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface. cell membrane, also called plasma membrane, thin membrane that surrounds every living cell, delimiting the cell from the environment around it. Transcription occurs in nucleus and then translation occurs in cytoplasm.Īll aerobic, but some facultative anaerobes by secondary modification.īound to plasma membrane as composite chromatophores.Įnzymes packed in plastids bound by membrane. Nonessential prokaryotic genes are encoded on extra chromosomal plasmid. When present, chemically simple (includes cellulose and chitin). Chemically complex (typical bacterial cell wall includes peptidoglycan). Present in some cells that lack cell wall. Sterol and carbohydrate is present that serve as receptors.ĭo not carry out respiration and photosynthesis. Generally lack sterol and no carbohydrate.Ĭontain part of respiration and in some photosynthetic machinery. Although it should not be the main reason to donate, remuneration is an incentive for plasmapheresis. Donors can give plasma through plasmapheresis a maximum of 50 times per year. Plasma donors in Austria receive an average of 30 per donation. Simple structure composed of protein, flagellin.Ĭomplex with 9+2 structure of tubulin and other protein. In the U.S., the average payment per plasma donation is 80-85 including bonuses, said Hotchko. This membrane serves to separate and protect a cell from its surrounding environment and is. Larger size 80s, found on membranes as in endoplasmic reticulum 70s present in organelles such as chloroplast and mitochondria. The outer lining of a eukaryotic cell is called the plasma membrane. Enclosed by this cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) are the cell’s constituents, often large, water-soluble, highly charged molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and substances involved in cellular metabolism. Smaller size 70S, distributed in the cytoplasm. Performs the function of Golgi bodies and mitochondria and also help in the separation of chromosome during cell division. Usually single circular without histones. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus are present. Nucleus lack nuclear membrane and nucleolus.
Mostly unicellular(some cyanobacteria may be multicellular). Eukaryotic organisms are those organisms which have true nucleus with nuclear and nucleolus and also contain all membrane bound cell organelles.ĭifferences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells Features prokaryotic and Eukaryotic.Prokaryotic organism are those which lacks true nucleus and membrane bound cell organelles. Please Rate 0 1 2 3 4 5 Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cellsĭepending on the internal structure of cell, organisms are divided into two types i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
